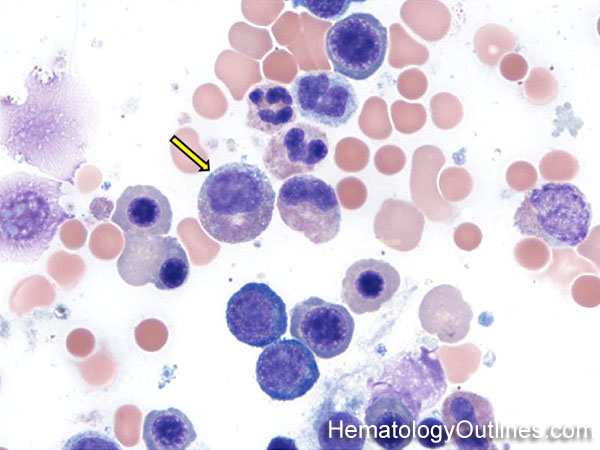
Blood/Blood Cells and Cellular Components ›› Neutrophils ›› Abnormal
Myelocyte*
 Click Here for Full Size Click Here for Full Size
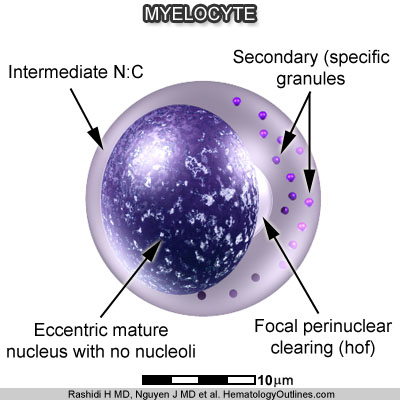
 › Microscopic Features:- 2-3x larger than a mature RBC
- Intermediate nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (more cytoplasm than promyelocyte)
- Eccentrically placed oval Nucleus (No nucleus indentation) with more mature chromatin (clumped)
- Perinuclear clearing is common
- Nucleoli are absent (Note: nucleoli are absent from this stage onward)
- More cytoplasm with only rare or absent primary (azurophilic) granules
- Secondary (specific) granules of neutrophilic (lilac), eosinophilic (red-orange), or basophilic (blue) color are present based on precursor type
 › Normal % blood-PB, marrow-BM, lymphoid tissue-LN:- PB: None
- BM: ~10%
- LN: None
 › May Resemble:
 › Differential Diagnoses:
If in blood or increased numbers in bone marrow:
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
Leukemoid reaction
Post GCSF therapy
Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia |
 › Classic Immunophenotype:- CD34-
- CD117-
- HLA-DR-
- CD13+
- CD33+
- CD15+
- CD11b+/-
- CD16-
- MPO+
 › Cartoon Image:
 Click and drag
Click and drag

for direct comparison › Misc:- Maturation step that comes after promyelocyte and precedes metamyelocyte
|